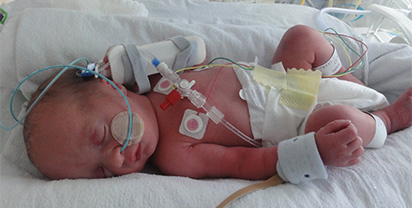
Vera Institute of Justice Final Report (2009): 80 NYC Foster Children Died in AIDS Drug Trials
Background: Between 1985 and 2005, at least 532 infants and children in New York City were conscripted as human subjects of clinical trials testing experimental AIDS drugs and vaccines. The New York City Agency for Child Services (ACS), the custodian of foster care children, gave agencies such as Incarnation Children’s Center,…